Yes, ok, I probably am a tad obsessed with Bluebird and Donald Campbell, and his very large support team’s world land speed, 403.10mph record run at Lake Eyre, South Australia on July 17, 1964.
The problem is that every now and again one of my countrymen pop up another batch of photos on social media, in this case Colin ‘Sporty’ Moran’s collection. What makes the photographs a bit different are the wheels-off suspension stuff – which are pretty rare.

I rather like rock-star F1 designer Adrian Newey’s perspective on Bluebird’s place in the ‘racing car’ pantheon published in Racecar Engineering in 2012:
“I think in terms of one of the biggest advances made, although it was not strictly speaking a racing car, was Bluebird. Arguably for its time it was the most advanced vehicle.” The Bluebird Proteus CN7 was the Ken and Lewis Norris designed car that Donald Campbell used to set a record of 403.1mph in July, 1964, the last outright land speed record car that was wheel driven.
It was a revolutionary car that featured an advanced aluminium honeycomb chassis, featured fully independent suspension and four-wheel drive. It also had a head-up display for Campbell. “It was the first car to properly recognise, and use, ground effects. The installation of the jet turbines is a nightmare, and it was constructed using a monocoque working with a lot of lightweight structures. It was built in a way that you build an aircraft, but at the time motor racing teams weren’t doing that.”
The car featured a Bristol-Siddeley Proteus 705 gas turbine engine which developed over 4,000bhp. It was a two-spool, reverse flow gas turbine engine specially modified to have a drive shaft at each end of the engine, to separate fixed ratio (David Brown made) gearboxes on each axle. It was designed to do 500mph, but surface conditions, brought about by adverse weather in 1963 and 1964, meant that its fastest recorded time was nearly 100mph short of its hypothetical capability.
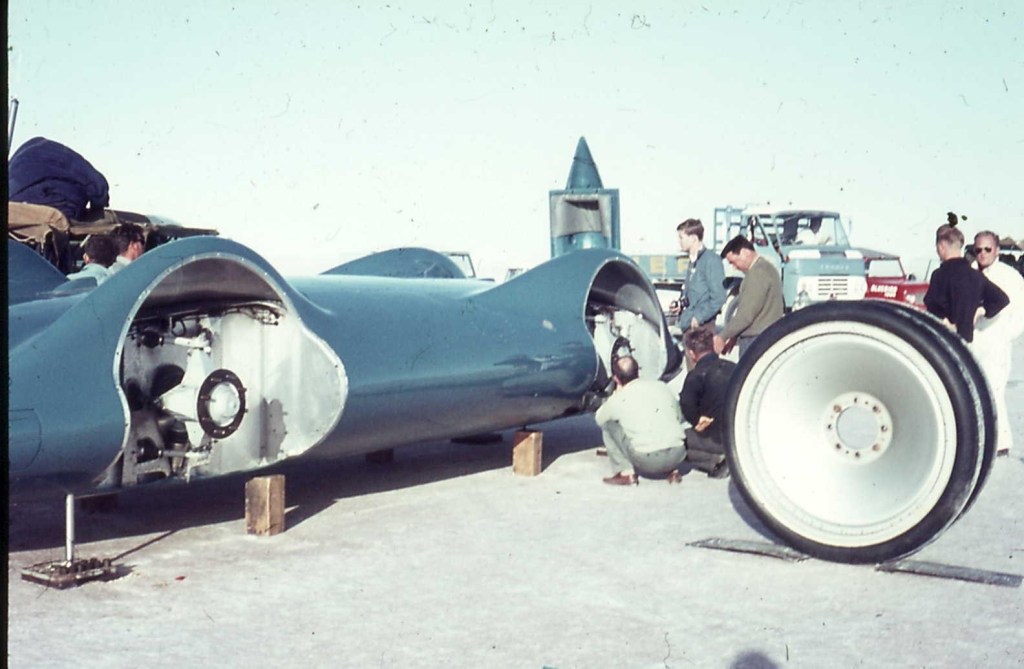
Look at the size of those uprights! Suspension by way of upper and lower wishbones front and rear and oleo-pneumatic struts, huge (420mm) Girling disc brakes are inboard and out of sight. Those mega Dunlop split-rim disc wheels are 52 inches (130cm) in diameter to give you a sense of size perspective.
Love the high-tech axle stands, lovely sense of backyard mechanic about them little jiggers!

Another rare reveal.
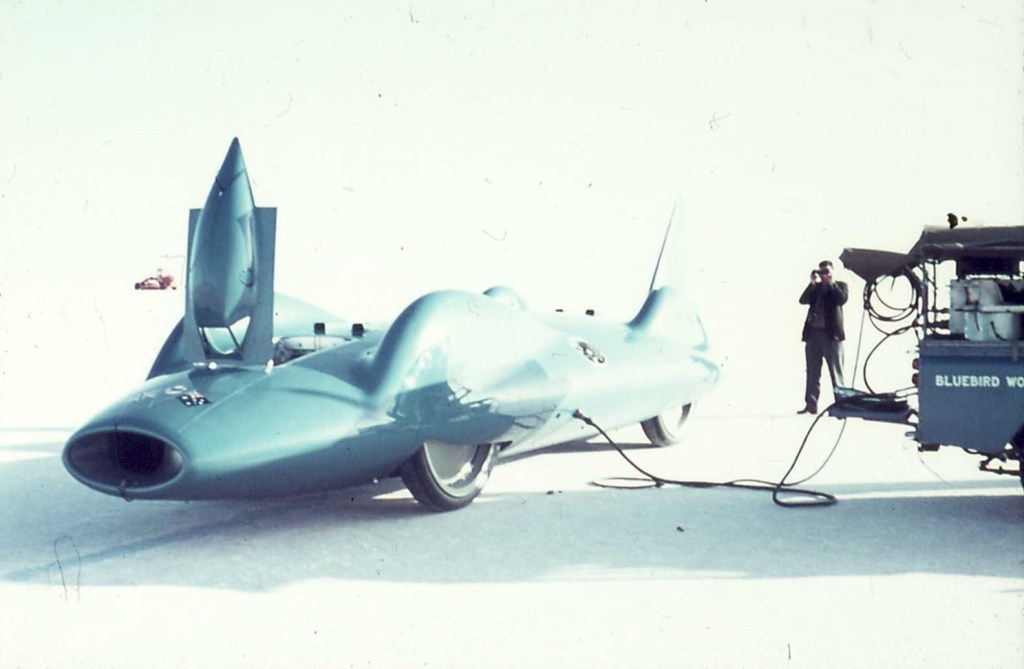
The man re-loading the braking parachute (wonder what speed Campbell could pop that?) is Ken Reakes. That gorgeous, high stabilising fin was added after Campbell’s massive 360mph Daytona shunt in September 1960. He fractured his lower skull, suffered a contusion of the brain, broke an ear drum, had cuts and abrasions and most critically, his confidence was shattered big-time. The car was rebuilt by 1962, as was his mental health, a process aided by gaining his pilot’s licence.
We get a nice glimpse of the Motor Panels, Coventry, chassis honeycomb inside that inspection/access panel, note also the exhaust ducts for the Proteus gas-turbine engine. Motor Panels was a subsidiary of Sir Alfred Owen’s Rubery Owen Holdings Group, which also included the BRM F1 manufacturing facility and team.
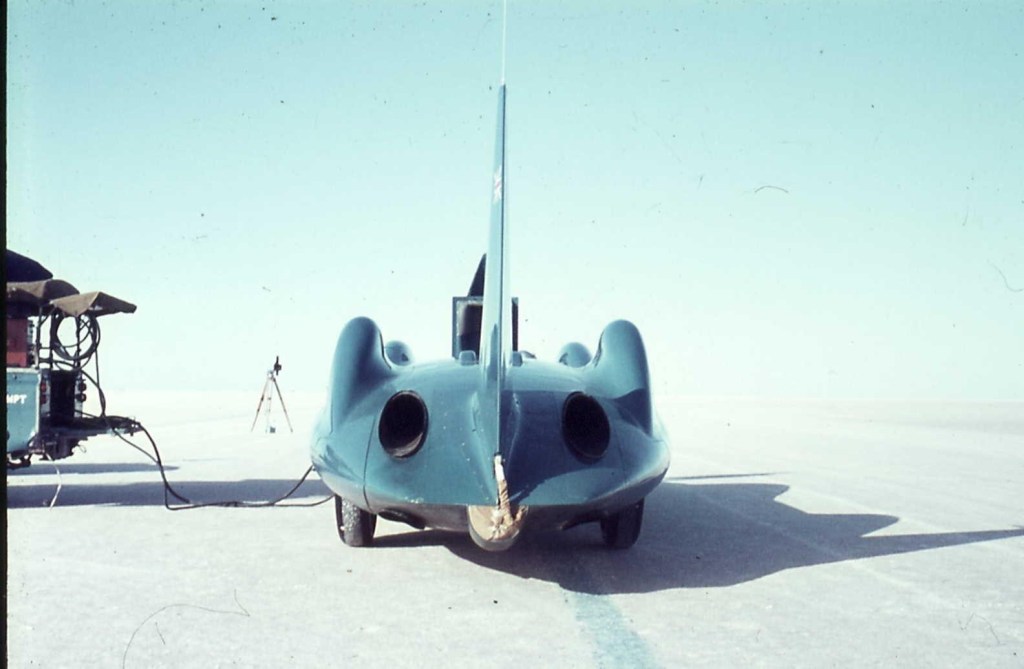
That is a timing beam, and a blue line, so we are lined up for a practice run.
Etcetera…
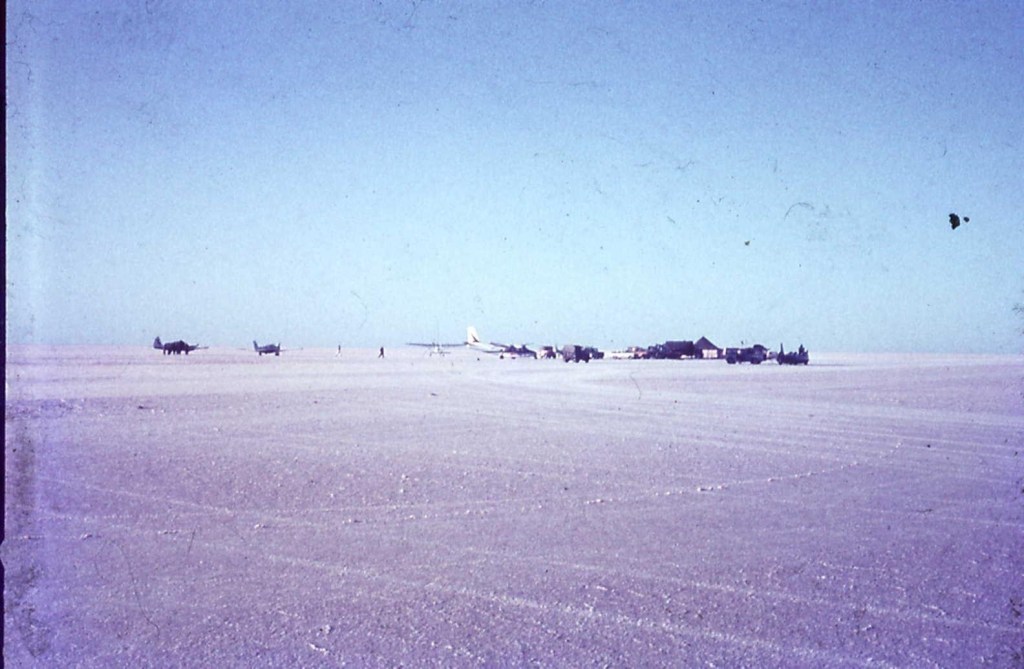

The utter desolation of ‘Camp Campbell’ on the vast Lake Eyre salt, 700km north of Adelaide – a most inhospitable and inaccessible place, to say the least.
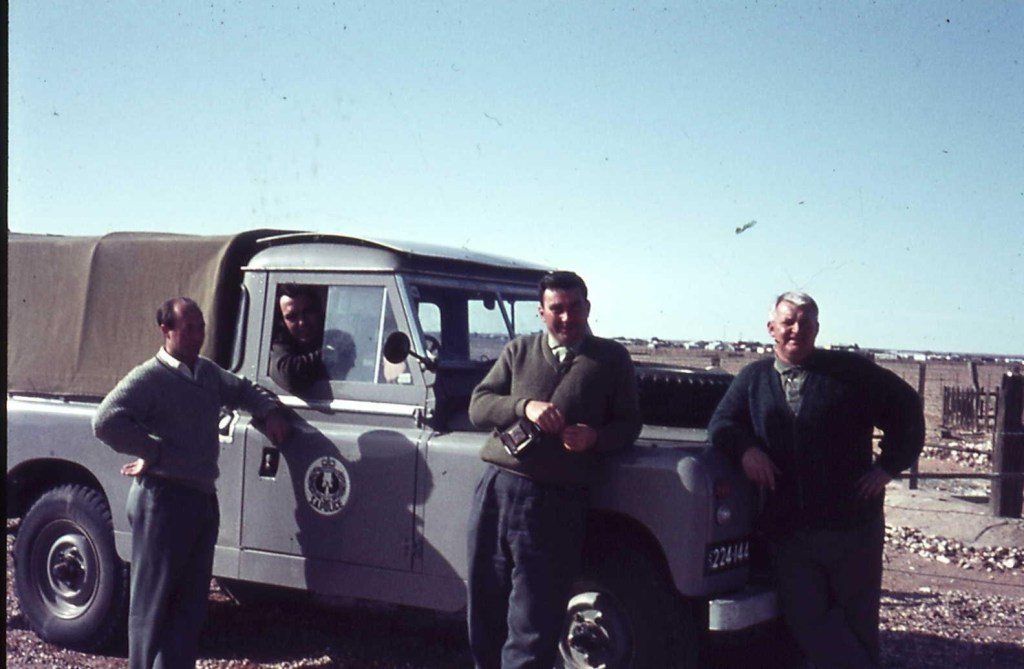

Likely lads at Muloorina Station, a 4000 square km sheep and cattle farm on the edge of Lake Eyre; two chaps, Colin Moran and Ken Wain, these lads are/were from the Maffra/Sale area in Gippsland, Victoria.
Campbell’s entourage of about 500 technical, support and media people were accommodated there in 1963 and 1964.
Credits…
Colin Moran
Tailpiece…
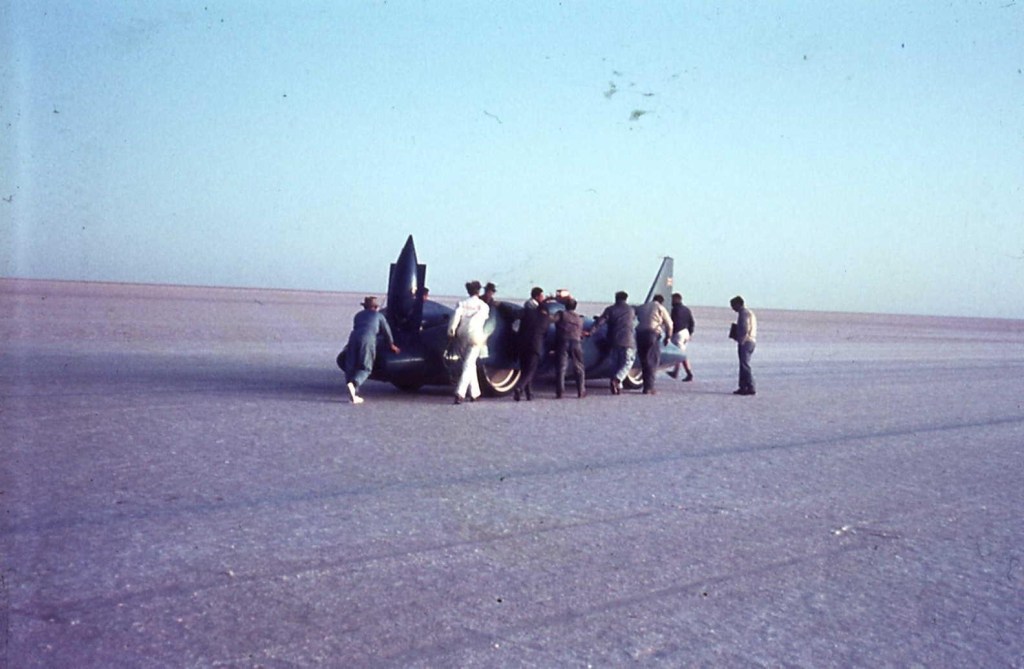

Only 4064kg to push around, too easy. The nose erection is the cockpit canopy, which of course pivots to the rear.
Finito…












