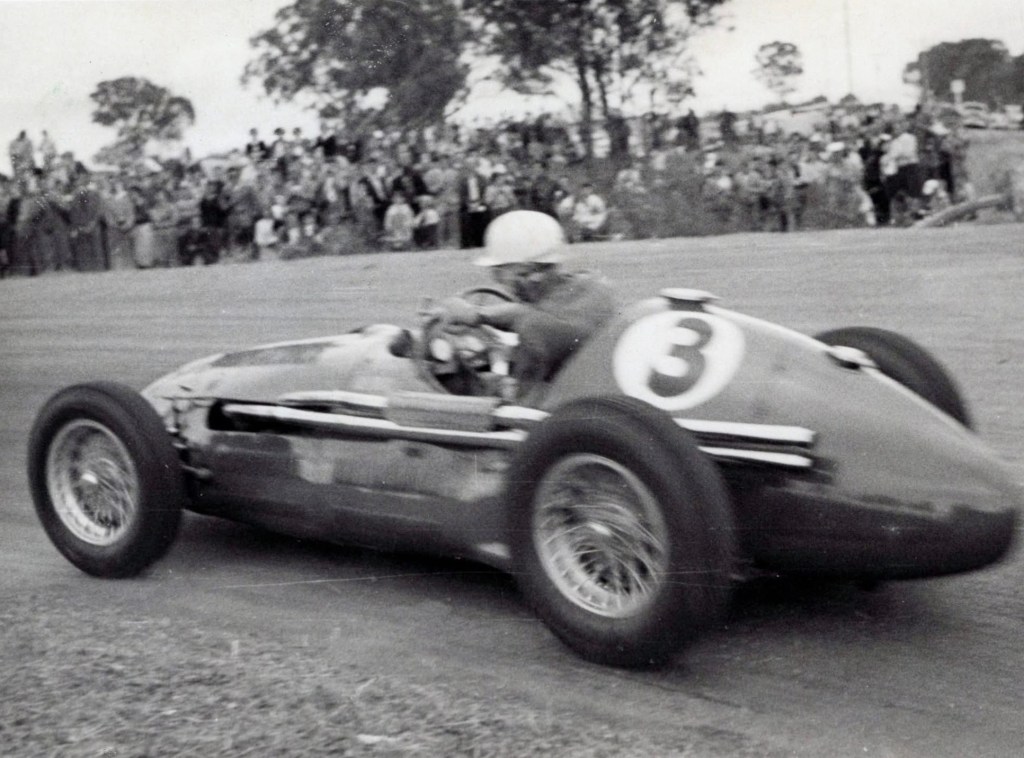

Easter 1955…
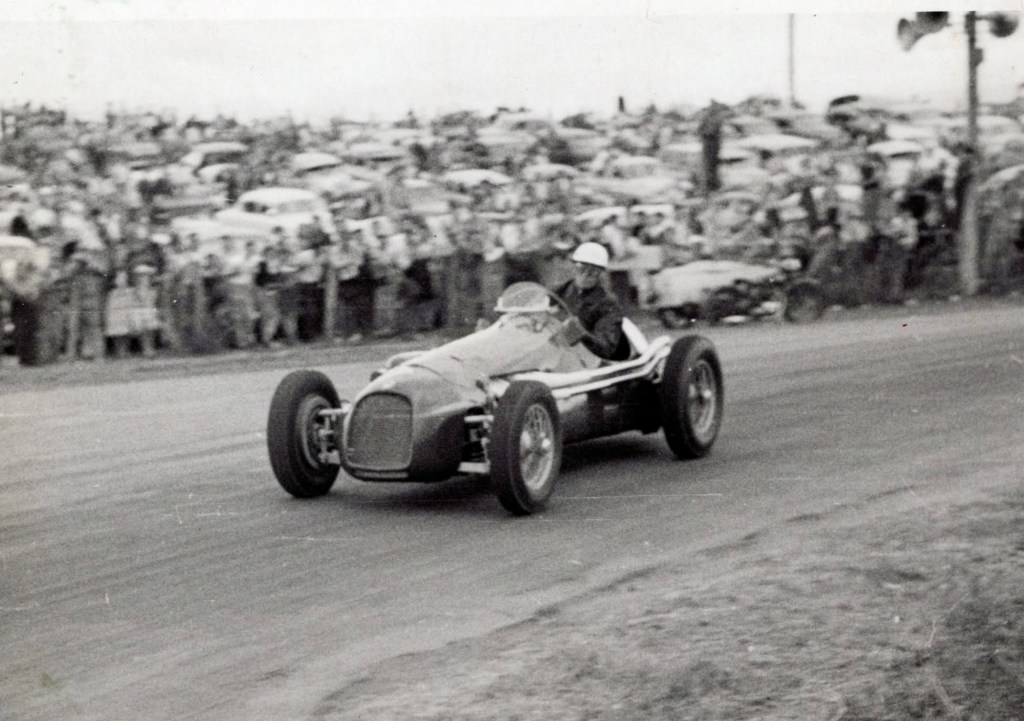
Reg Hunt working his Maserati A6GCM-250 hard at the Bathurst Easter meeting in 1955.
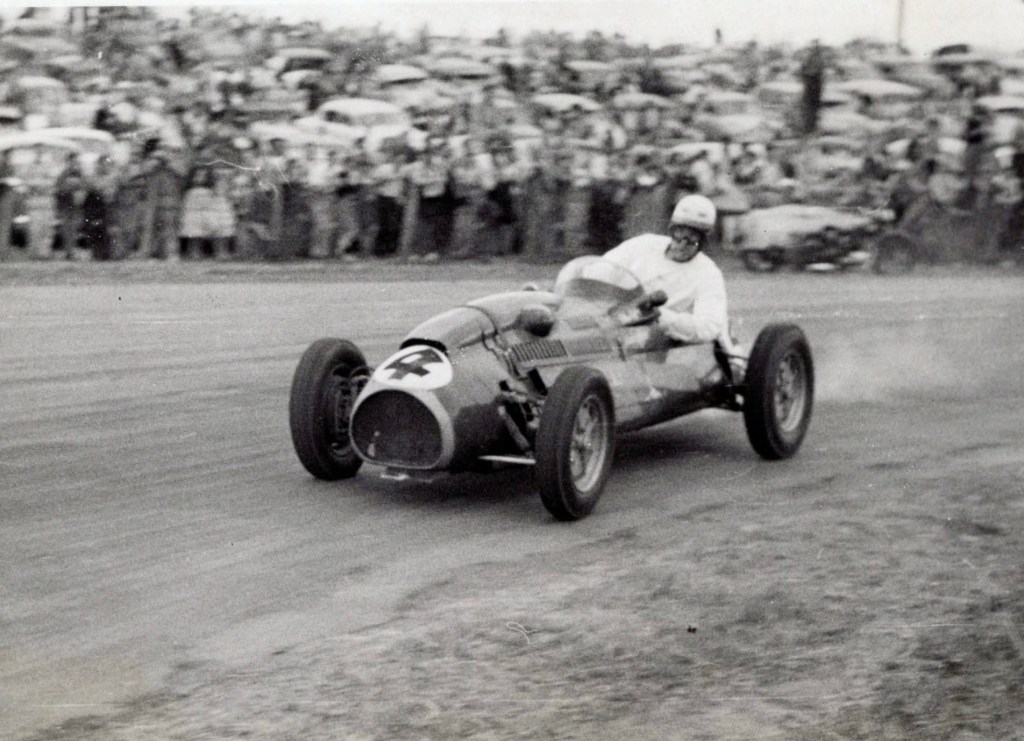
He won the 26 lap Bathurst 100 feature from Ern Seeliger aboard Stan Jones’ ex-Jack Brabham Cooper T23 Bristol and Lex Davison’s HWM Jaguar, below.
Clive Adams’ drove Stan Coffey’s Cooper T20 Bristol skilfully but lost an early joust for third place with Davison, spinning at Forrest’s Elbow on the run down the mountain.
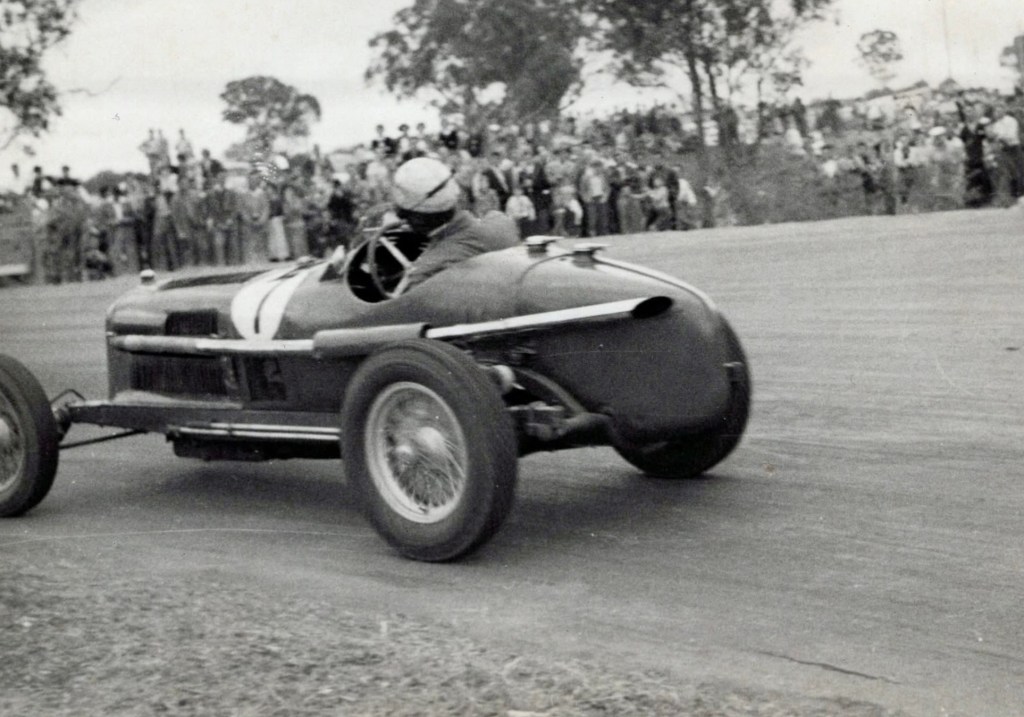
By 1955 the ex-Jack Saywell Alfa Romeo P3 had passed through the hands of Julian Barrett and Bill Murray and was powered by an Alvis engine. Sold by Murray to Gordon Greig, the car was involved in a terrible accident after Greig pitted, feeling sick, on lap 16.
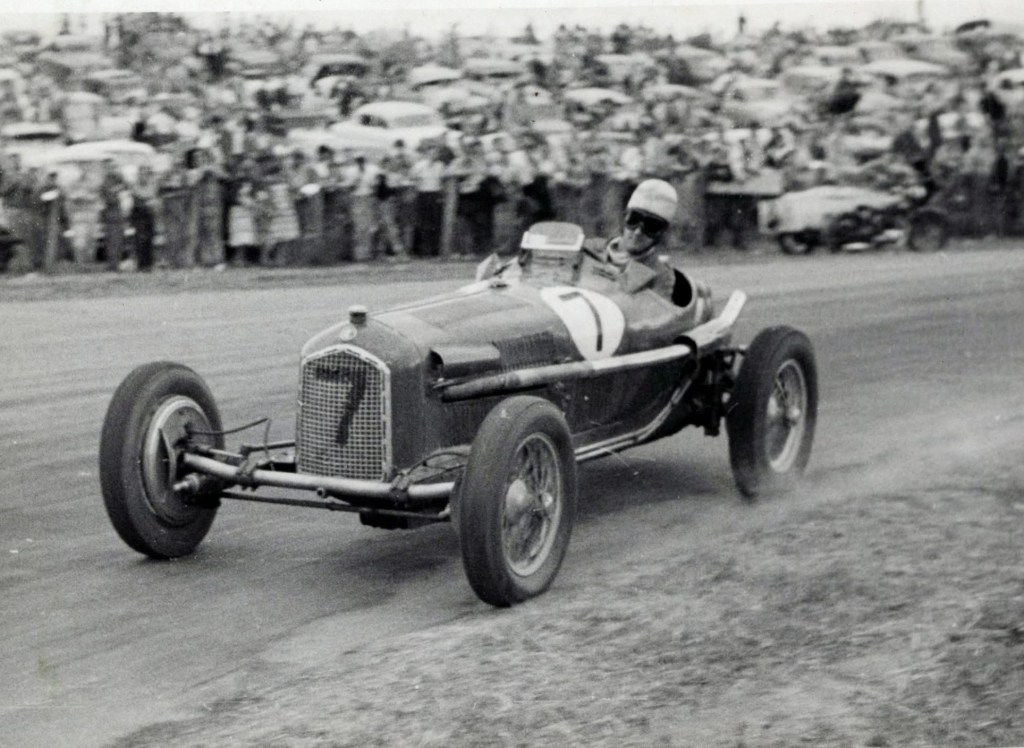

Tony Bourke, one of Greig’s crew, jumped aboard to finish the race and promptly lost control of the car over Conrod’s final hump, spun and went backwards off the track through the crowd killing one, mortally wounding another and injuring 20. Bourke stepped from the car unhurt and was later treated for shock.
Changes were were made to eliminate spectators from this area after the Coroner’s Inquest and public and press reaction. Bourke died after a Midget crash at Westmead Speedway in 1965.

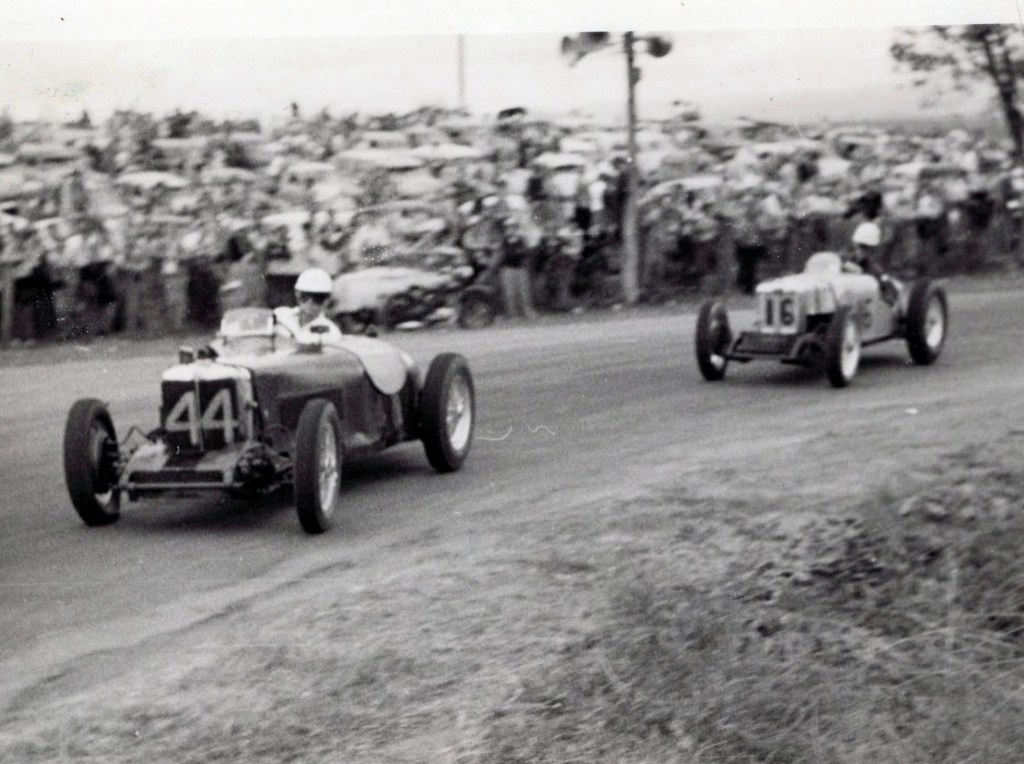
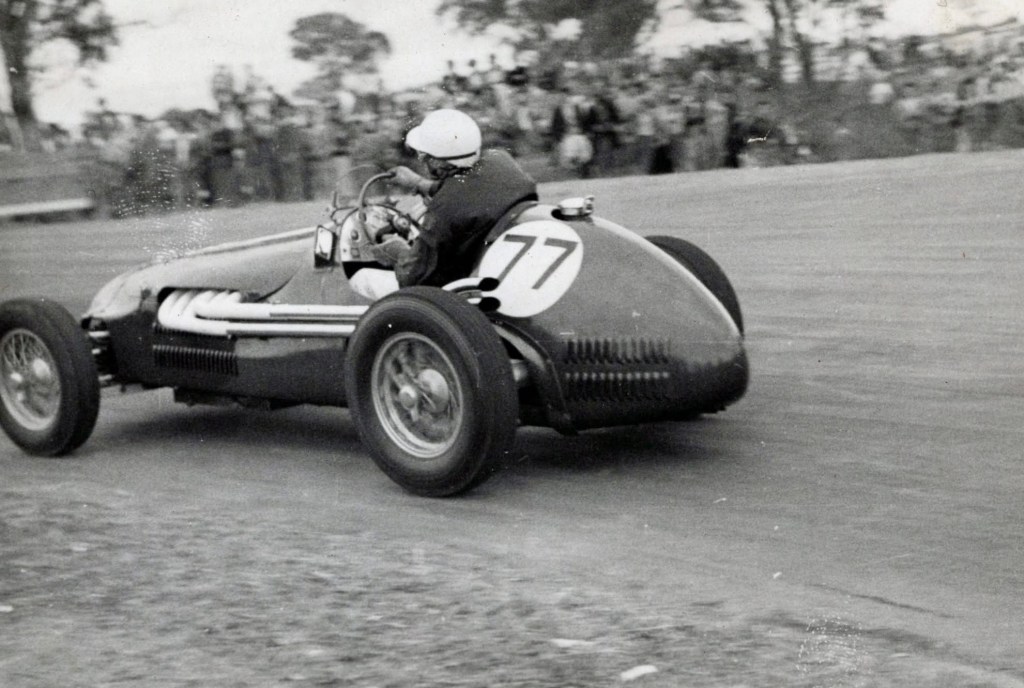
Col James MG Spl s/c and Ray Fowler, MG Spl, negotiate Hell Corner in the Group B Racing Car Scratch. They were third and fourth in this 3 lapper won by Stan Jones’ Cooper 1100.

Tom Jordan’s 1949 2.5-litre Riley engined Healey Silverstone (above) ‘was raced as a factory entry by Tony Rolt in the UK in 1949, then raced by Charles Mortimer in 1950 – he wrote a book about it, Racing a Sports Car – and was then returned to the factory, bought by Queenslander Colin Leagh Murray and raced and hillclimbed by him in Queensland before being sold to Jordan who had many successes with the car,’ wrote John Medley.
Etcetera…

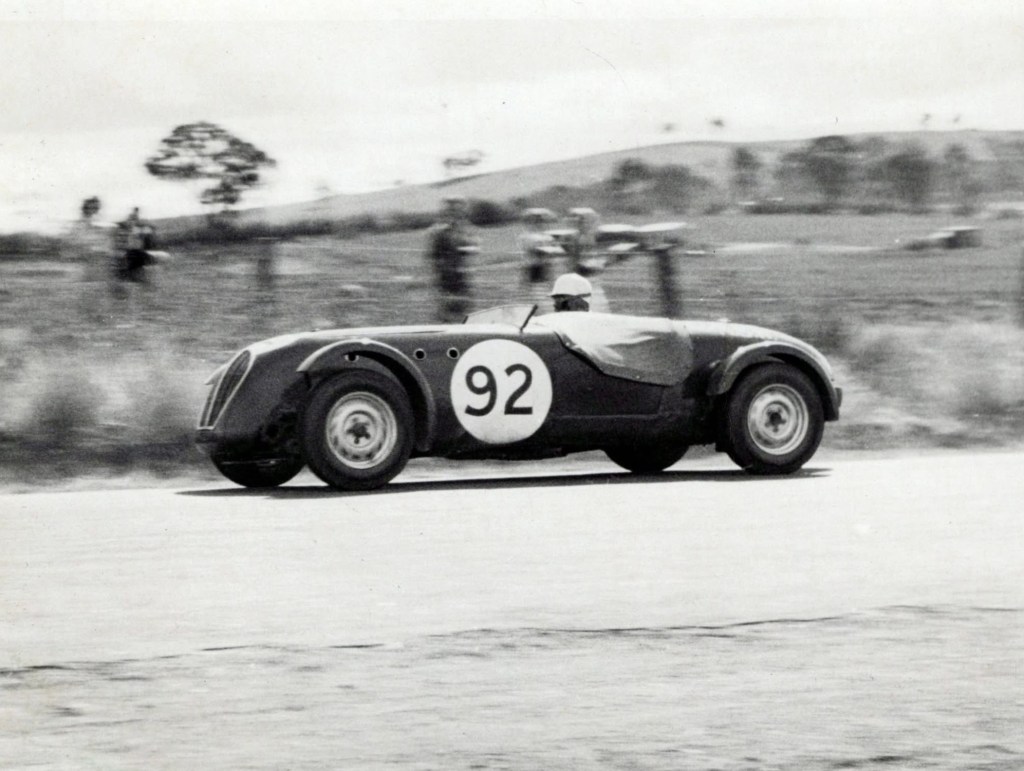
It’s doubtful that Lex would have listed the HWM Jaguar – an ex-Moss HWM Alta 2-litre F2 chassis – amongst his favourite cars but he and his team coaxed enough speed and reliability out of the C-Type Jaguar powered jigger to win the 1954 AGP at Southport, aided and abetted by the breakage of a chassis weld on Maybach 2 when Stan Jones seemingly had the race ‘in the bag’.
By 1955 the HWM Jag was off the ultimate pace, Hunt had reset the local bar with his Maserati and Lex would meet the challenge in early 1956 with the purchase of Tony Gaze’ Ferrari 500/625 3-litre.
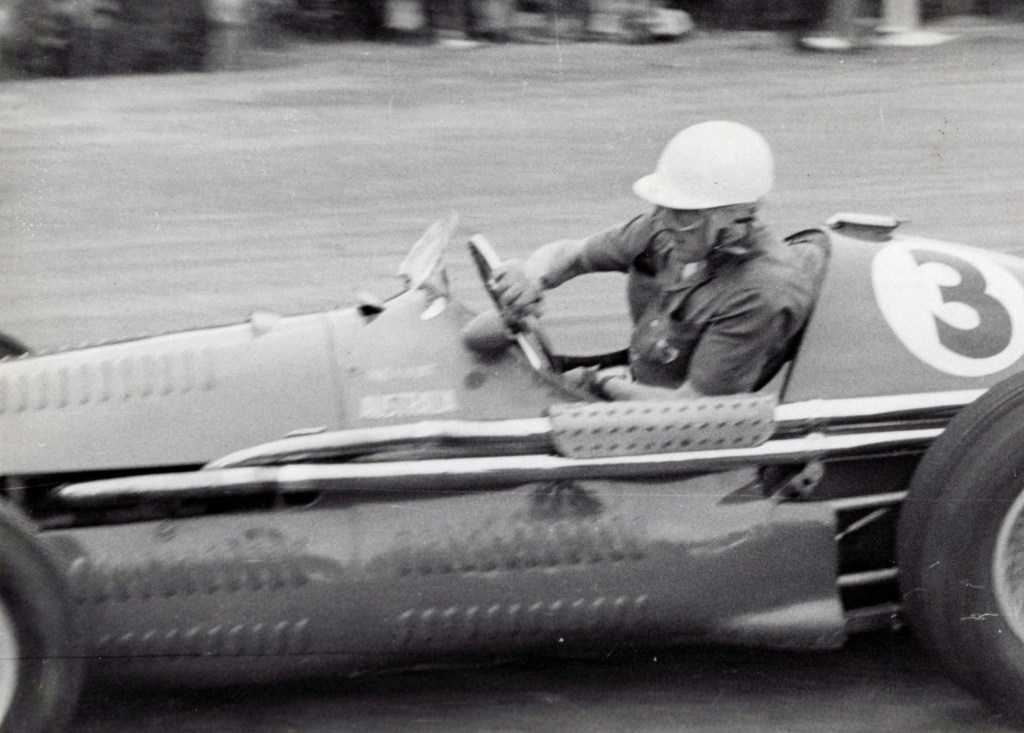

October 1955…
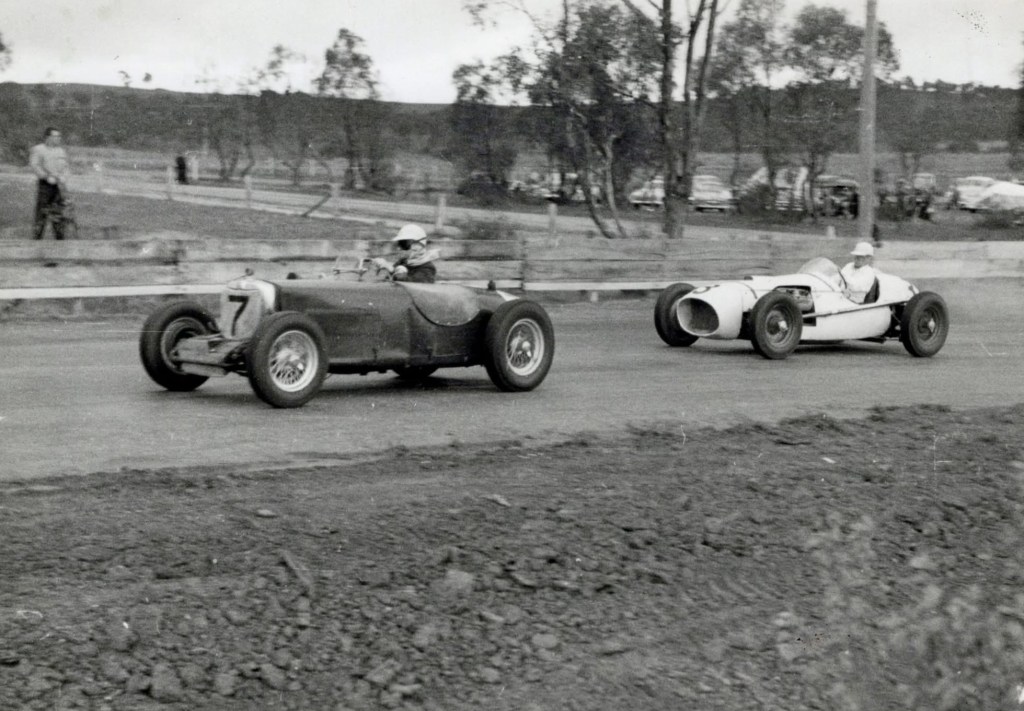

C James MG Spl S/c from Ted Gray, Tornado Ford, Hell corner, during the 3 lap Group A Racing Car Scratch.
On the last lap Tiger Ted lost the new car coming down the mountain near Griffin’s destroying it and hospitalising himself for months. Tornado 2 Ford would emerge in due course and Tornado 2 Chev became the fastest car in the country by later 1957, read here: https://primotipo.com/2015/11/27/the-longford-trophy-1958-the-tornados-ted-gray/
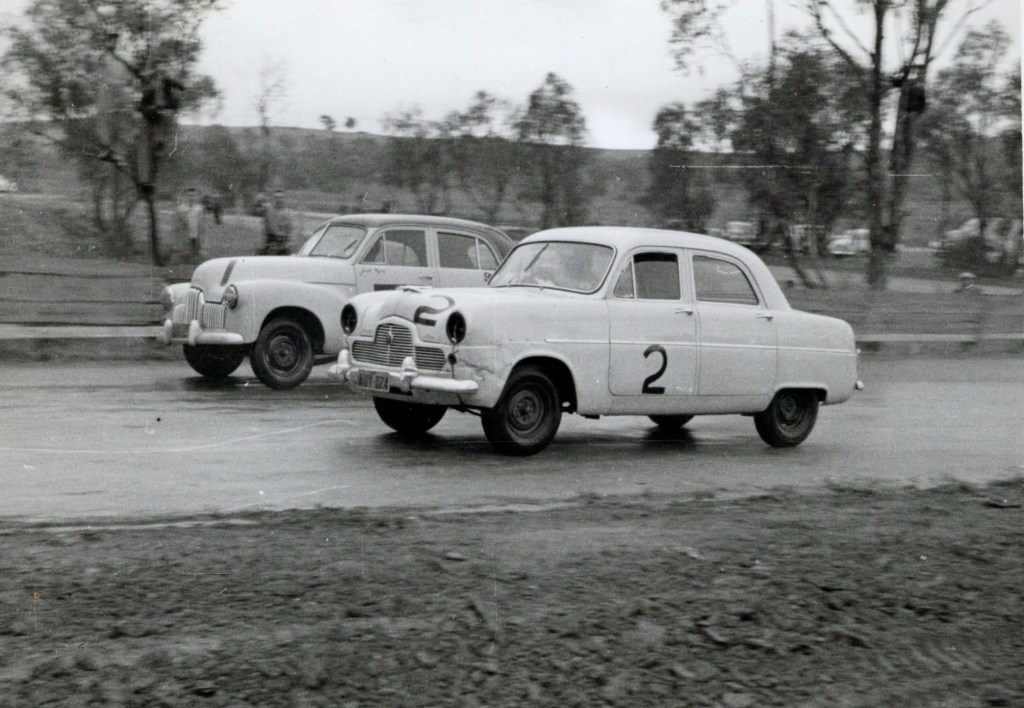

Touring car racing was steadily gaining in popularity with Jack Myers easily winning the sedan car handicap in his well developed, black-roofed, yellow Holden 48-215. ‘Holden wonder-man of the mid-1950s’ as John Medley described him. Here he is alongside George Pearse’s Ford Zephyr. See here for more on Jack: https://primotipo.com/2024/05/02/jumpin-jack-myers/

Jack Robinson’s Jaguar XK120 Special.
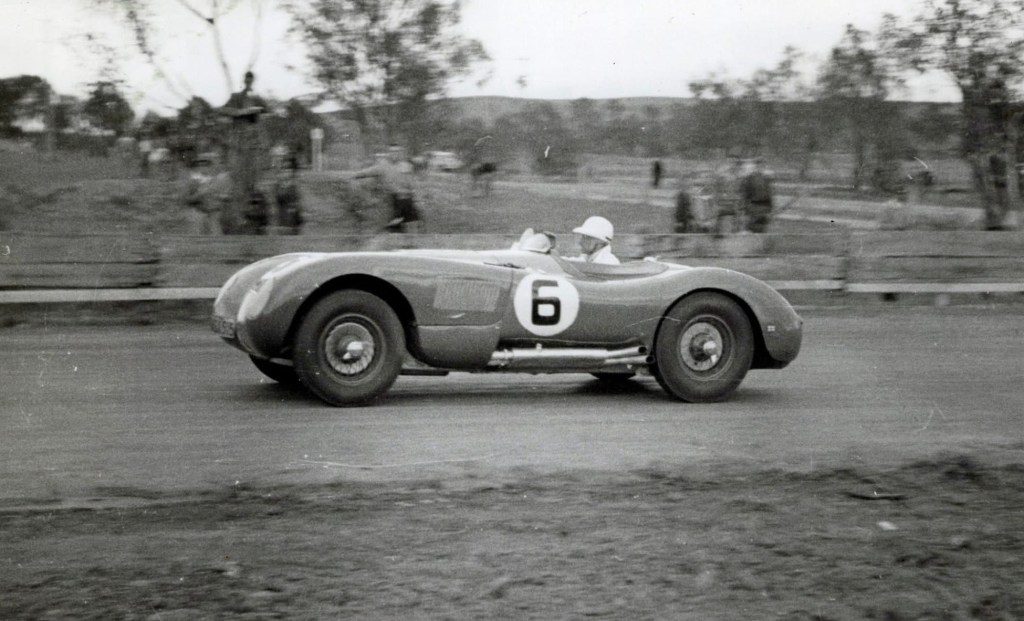

Dr John Boorman on the rise out of Hell corner on his way up Mountain Straight, ‘off scratch in the 6 lap Sports Car Handicap made no impression at all on Shmith’s new Austin Healey 100S which did 124mph through the timed quarter while Boorman did 125,’ Medley wrote. More about this car here: https://primotipo.com/2014/08/05/gnoo-who-gnoo-blas-circuit-jaguar-xkc-type-xkc037/
Postscript: Easter Bathurst tragedy…
After publishing this article, journalist/historian Ray Bell emailed me excerpts from ’emails I sent to the sister of Gavin Larnach’, one of the Bathurst accident victims.
1. That this whole thing is surrounded by lies and cover-ups is simply disgraceful. One can readily understand Mark’s state of mind and applaud him on his pursuit of the facts.
One such fact is that this car was very unstable after it had the very heavy Alvis engine installed. Ray Wamsley told me this, he was the next owner of the car, and he said it was absolutely transformed when he fitted a GMC truck engine after the Alvis unit failed.
2. I’ve subsequently spoken a journalist of the time, about the cover-ups. He told me that he always understood it was the local member who pushed for the hushing of everything with a view to ensuring that the racing wasn’t shut down. The local member was Gus Kelly, who was a Cabinet member with some influence and had been the local member for many years, so that makes sense.
Two factors come into play here. In 1946 there was difficulty getting the racing off the ground because of police resistance. Additionally, a driver and a spectator had been killed at the Gnoo Blas race meeting in January, 1955. The fear throughout the two organising clubs would have been quite pronounced and it was just eighteen months later that the whole of motor racing in NSW had to comply with the new Speedways Act, which introduced standards for safety fencing etc.
3. What is really bugging me is John Medley’s comment that someone who gave evidence wasn’t actually in the country when the crash occurred. Not so consequential if he was just giving evidence about something technical, but still it appears from John’s comment that it might matter.
Credits…
Ian Arnold photographs via his son Mark Arnold
Finito…

























